Administrative law may sound complicated, but it plays a big part in our daily lives—even if we don’t notice it. Whether it’s about getting a driver’s license, applying for social security, or understanding how public rules are made, administrative law helps keep things fair and organized. This easy guide will walk you through everything you need to know about administrative law in simple terms.
What is Administrative Law?
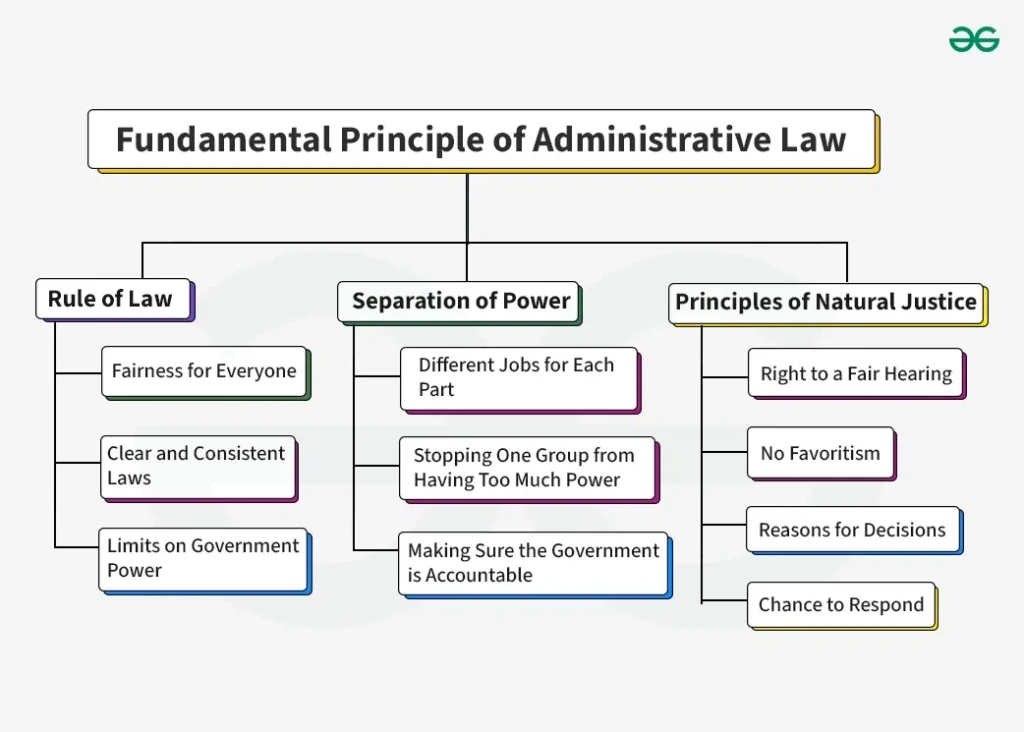
Administrative law is a branch of public law that governs the activities of government agencies. These agencies make rules, enforce them, and sometimes even judge cases related to them. Think of it like a set of rules for the people who make the rules!
Instead of courts and police handling every matter, the government has many administrative agencies—like the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)—that help manage different parts of public life. Administrative law keeps those agencies in check so they don’t misuse their power.
This law ensures that agencies act fairly, follow the law, and respect the rights of citizens. It covers things like rule-making, licensing, benefits, permits, and discipline actions by government officials.
Why Do We Need Administrative Law?
Without administrative law, government agencies could make unfair decisions without being questioned. Administrative law acts like a referee, making sure agencies follow fair processes and give people a chance to speak up.
Imagine you applied for a building permit, and the city said “no” without giving you a reason. Administrative law says you have a right to understand that decision and appeal it if necessary. It also forces agencies to make decisions based on law—not on personal opinions or bias.
In short, administrative law protects fairness, transparency, and accountability in the way the government operates.
Who Uses Administrative Law Every Day?
You might be surprised, but administrative law affects nearly everyone—even if they’ve never heard of it. From businesses to students, everyone interacts with government rules in some way.

How it Helps Citizens
Citizens use administrative law when:
- Applying for disability benefits
- Filing for unemployment
- Challenging parking tickets
- Requesting public records
- Reporting unsafe housing
Thanks to administrative law, people have the right to a fair administrative law notes and can appeal government decisions.
How it Helps the Government
For government workers, administrative law provides a clear path to follow. It helps agencies make decisions in a consistent way and explains what steps they must take. For example:
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) uses administrative law to approve medicines.
- The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) applies tax rules created through administrative procedures.
It keeps things organized and avoids chaos in public services.
Real-Life Examples
Let’s look at some real examples where administrative law matters:
- Case 1: A student applies for financial aid, but the agency denies it. The student appeals using administrative procedures and wins.
- Case 2: A business is fined for not following safety rules. The company challenges the fine and gets it reduced.
- Case 3: A homeowner disagrees with a zoning change in their neighborhood and files a complaint with the city planning board.
All these situations are guided by administrative law rules and processes.
Basic Terms You Should Know
Let’s break down some of the common terms in administrative law:
- Agency: A part of the government responsible for specific tasks (like the DMV).
- Regulation: A rule made by an agency that affects people’s rights or actions.
- License: Legal permission to do something, like driving or opening a restaurant.
- Notice: When an agency tells you it’s making a new rule or decision.
- Hearing: A chance for someone to explain their side before an agency makes a final decision.
- Due Process: Your right to be treated fairly when the government makes decisions that affect you.
Knowing these basic words makes it much easier to understand administrative law.
How Rules Are Made in Administrative Law
Administrative agencies don’t just make up rules overnight. There’s a process called “rulemaking.” Here’s how it usually works:
- Proposal: The agency creates a draft of the rule.
- Public Notice: The draft is shared so the public knows what’s coming.
- Comments: People, businesses, or experts can send feedback.
- Final Rule: After reviewing comments, the agency publishes the final version.
This process is required by the Administrative Procedure Act (APA) in the U.S., which sets the standard for how rules must be made. It ensures public participation and limits abuse of power.
What Happens When You Disagree With a Rule?
Sometimes, people or businesses don’t agree with what an agency decides. Luckily, administrative law gives you the right to challenge those decisions.

Appeal in Simple Words
An appeal is when you ask a higher authority to review a decision. In administrative law, this often means you can ask the agency itself—or another body—to take another look at your case.
For example, if your application for housing assistance is denied, you can request a hearing. There, you get to explain your side and provide evidence.
Administrative Court Role
If the agency still stands by its decision, you might be able to take the case to an administrative law judge (ALJ). These judges don’t work for the agency and are supposed to be neutral.
Administrative courts hear cases like:
- Social Security benefit denials
- Immigration decisions
- Medicare disputes
They follow simpler procedures than regular courts, making the process faster and more focused on facts.
Key Features of Administrative Law
Some of the main features that make administrative law unique include:
- Efficiency: Faster than regular courts
- Expertise: Agencies specialize in specific areas
- Flexibility: Procedures can be adapted to the situation
- Public Participation: People can share their views on rules before they’re final
- Checks and Balances: Agencies can’t just do whatever they want—they must follow laws
Easy Notes for Quick Revision
Need to revise quickly before an exam or interview? Here’s a simple recap:
- Administrative law controls how government agencies operate.
- It protects citizen rights and ensures fair procedures.
- Agencies can make rules, grant licenses, and punish violators.
- If you disagree with a decision, you can appeal.
- Administrative law is used daily by students, workers, businesses, and government bodies.
Keep these key points in mind, and you’ll have a solid understanding of the topic!
The Bottom Line
Administrative law may seem like a hidden part of the government, but it touches our lives more than we realize. From applying for school aid to filing for taxes or reporting environmental violations, this law is the system that keeps public services running smoothly and fairly.
It ensures that government decisions are not only legal but also reasonable, consistent, and respectful of individual rights. Whether you’re a student, a small business owner, or just someone trying to renew a driver’s license, administrative law is there to protect you.
By learning these administrative law notes, you’re gaining the tools to understand your rights and responsibilities as a citizen. And that’s something everyone—even a 10-year-old—can benefit from.